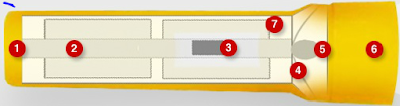
1 - Case The tube that homes the elements of the torch, as well as the batteries and lamp (light bulb).
2 - Contacts a really skinny spring or strip of metal (usually copper or brass) that's set throughout the torch, creating the electrical affiliation between the assorted elements – the batteries, the lamp, and also the switch. These elements conduct electricity and "hook everything up," finishing the circuit.
3 - Switch The flow of the electricity is activated after you push the switch into the ON position, providing you with lightweight. The flow of electricity is broken once the switch is pushed into the OFF position, therefore turning off the sunshine.
4 - Reflector A plastic half, coated with a shiny metallic element layer that rests round the lamp (light bulb) and redirects the sunshine rays from the lamp to permit a gradual ray, that is that the lightweight you see emitting from the torch.
5 - Lamp the sunshine supply in a very torch. In most flashlights, the lamp is either a W filament (incandescent bulb) or a light-weight emitting diode (solid state bulb), additionally called associate degree crystal rectifier. The W filament or crystal rectifier glows once electricity flows through it, therefore manufacturing actinic ray. W|metal} may be a natural element and also the W filament may be a terribly skinny wire. W lamps should be replaces once the W filament breaks. associate degree crystal rectifier contains a really little semiconductor (diode) that's encapsulated in epoxy and this half emits lightweight once electricity flows through it. LED's om flashlights ar wide thought of "unbreakable" and not replaced – a period lamp.
6 - Lens The lens is that the clear, plastic half you see on the front of the torch that protects the lamp, since the lamp is created if glass and may simply be broken.
7 - Batteries once activated, the batteries are the ability supply for your torch.
Whether you’re outdoors for a nighttime journey or end up within the dark from an influence outage when a storm, the convenience of moveable lightweight is as shut as a straightforward button on your torch. however simply however will a torch work?
How do of these torch elements work together?
When the switch of a torch is pushed into the ON position, it makes contact between 2 contact strips, that begin a flow of electricity, battery-powered from the battery. The batteries are connected in such the simplest way that electricity (flow of electrons) runs between the positive and negative electrodes of the battery. The batteries rest atop atiny low spring that's connected to a contact strip. The contact strip runs down the length of the battery case and makes contact with one facet of the switch. there's another flat contact strip on the opposite facet of the switch, that runs to the lamp (light bulb), providing associate degree electrical affiliation. there's another half connected to the lamp that produces contact with the positive conductor of the highest battery, therefore finishing the circuit to the lamp and finishing the generation of electricity. One find here different shows about tactical flashlight.
When activated by electricity, the W filament or crystal rectifier within the lamp begins to glow, manufacturing lightweight that's visible. This lightweight reflects off of the reflector that's positioned round the lamp. The reflector redirects the sunshine rays from the lamp, making a gradual beam of sunshine, that is that the lightweight you see emitting from the torch. a transparent lens covers the lamp on your torch so the glass on the lamp doesn't get broken.
When the torch switch is then pushed into the OFF position, the 2 contact strips ar physically stirred apart and also the path for the electrical current is broken, therefore ending the assembly of sunshine, and turning your torch off.
All of the on top of elements should be connected and in situ so as for the moveable torch to figure. Otherwise, you've got associate degree electric circuit and also the electricity won't flow.
2 - Contacts a really skinny spring or strip of metal (usually copper or brass) that's set throughout the torch, creating the electrical affiliation between the assorted elements – the batteries, the lamp, and also the switch. These elements conduct electricity and "hook everything up," finishing the circuit.
3 - Switch The flow of the electricity is activated after you push the switch into the ON position, providing you with lightweight. The flow of electricity is broken once the switch is pushed into the OFF position, therefore turning off the sunshine.
4 - Reflector A plastic half, coated with a shiny metallic element layer that rests round the lamp (light bulb) and redirects the sunshine rays from the lamp to permit a gradual ray, that is that the lightweight you see emitting from the torch.
5 - Lamp the sunshine supply in a very torch. In most flashlights, the lamp is either a W filament (incandescent bulb) or a light-weight emitting diode (solid state bulb), additionally called associate degree crystal rectifier. The W filament or crystal rectifier glows once electricity flows through it, therefore manufacturing actinic ray. W|metal} may be a natural element and also the W filament may be a terribly skinny wire. W lamps should be replaces once the W filament breaks. associate degree crystal rectifier contains a really little semiconductor (diode) that's encapsulated in epoxy and this half emits lightweight once electricity flows through it. LED's om flashlights ar wide thought of "unbreakable" and not replaced – a period lamp.
6 - Lens The lens is that the clear, plastic half you see on the front of the torch that protects the lamp, since the lamp is created if glass and may simply be broken.
7 - Batteries once activated, the batteries are the ability supply for your torch.
Whether you’re outdoors for a nighttime journey or end up within the dark from an influence outage when a storm, the convenience of moveable lightweight is as shut as a straightforward button on your torch. however simply however will a torch work?
How do of these torch elements work together?
When the switch of a torch is pushed into the ON position, it makes contact between 2 contact strips, that begin a flow of electricity, battery-powered from the battery. The batteries are connected in such the simplest way that electricity (flow of electrons) runs between the positive and negative electrodes of the battery. The batteries rest atop atiny low spring that's connected to a contact strip. The contact strip runs down the length of the battery case and makes contact with one facet of the switch. there's another flat contact strip on the opposite facet of the switch, that runs to the lamp (light bulb), providing associate degree electrical affiliation. there's another half connected to the lamp that produces contact with the positive conductor of the highest battery, therefore finishing the circuit to the lamp and finishing the generation of electricity. One find here different shows about tactical flashlight.
When activated by electricity, the W filament or crystal rectifier within the lamp begins to glow, manufacturing lightweight that's visible. This lightweight reflects off of the reflector that's positioned round the lamp. The reflector redirects the sunshine rays from the lamp, making a gradual beam of sunshine, that is that the lightweight you see emitting from the torch. a transparent lens covers the lamp on your torch so the glass on the lamp doesn't get broken.
When the torch switch is then pushed into the OFF position, the 2 contact strips ar physically stirred apart and also the path for the electrical current is broken, therefore ending the assembly of sunshine, and turning your torch off.
All of the on top of elements should be connected and in situ so as for the moveable torch to figure. Otherwise, you've got associate degree electric circuit and also the electricity won't flow.
Comments
Post a Comment