Mercerising Machine, Washing Machine, Cold wash chamber, Pad steam machine, Cold Pad Batch (C.P.B), Jigger Machine
Mercerising Machine
Mercerising: Mercerising is the process by which the fabric is treated with NaOH solution to cause swelling of fibers. This results in improved lestre, strength and dye affinity. Cotton is mercerized under tension and all alkali must be washed out before the tension is released or shrinkage will take place .Mercerizing can take place directly on grey cloth or after bleaching .
Section of mercerizing machine:
1. Coustic Zone
2. Stabilizings Zone
3. Washing Zone
4. Drying Zone

Figure: Mercerising machine

Figure: benniger mercer
Washing Machine
Washing: Washing is the process to remove the impurities from the cloth. Water and soap are used as washing substance and also pH control.
Main chamber of machine:
1. Cold wash chamber
2. Hot wash chamber

Figure: Open-width washing machine
Cold wash chamber
Cold wash chamber: In this chamber the cloth is washed by cold water. It is placed on the two ends of the machine.

Figure: washing machine
Pad steam machine
Pad steam machine: Pad steam machine is one kind of washing machine. The basic difference from washing machine that pad steam machine contains a steamer. In pad steam the cloth pass through the steamer where the cloth is washed by steam at temperature 95-98°C and color fixation these zone. There are 20 rollers which are called dryer. The dryers are rotate by supplying power from motor by chain, gear and belt. The dryers dry the cloth by supplying steam from steam boiler. The clothes are collected by the quick return mechanism.

Figure: Pad steam machine
Application:
1. To mix the color fixation of the cloth
2. To wash the cloth
3. pH control
Cold Pad Batch (C.P.B)
C.P.B: C.P.B or Cold Pad Batch machine is one kind of one color dyeing machine. In C.P.B machine there are spinner roller, steel roller and rubber roller. The spinner roller reduces the folding of cloth and the friction of rubber roller to help the cloth to spin the roller. In C.P.B machine the cloth pass through the roller and below the roller there is a container. The mixture of deices and chemical (NaOH/Urea) by the ratio of 4:1 used to dyeing the cloth. The chemical and deices kept in separated tank and by the help of dozzins pump chemical and deices mixed I 4:1 in a container. From this container using dozzins pump the mixture sprayed on the cloth. By the help of rubber roller the mixture of chemical and deices mixed uniformly on cloth. Finally the cloth is dried by the roller dryer.
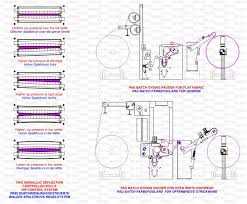
Figure: Cold Pad Batch Dyeing Machine

Figure: Cold Pad Batch Machine
Application:
It is used for dyeing (one color) cloth
.
Jigger Machine
Jigger machine: Jigger is a multipurpose machine used for dyeing, scouring, bleaching etc. This machine is used for small purpose generally used for processing sample/short quality dyeing.

Figure: Jigger Machine
Main parts of machine:
1. Hydraulic motor
2. Heat exchanger
3. Coil
4. Electric motor / Pump
Mercerising: Mercerising is the process by which the fabric is treated with NaOH solution to cause swelling of fibers. This results in improved lestre, strength and dye affinity. Cotton is mercerized under tension and all alkali must be washed out before the tension is released or shrinkage will take place .Mercerizing can take place directly on grey cloth or after bleaching .
Section of mercerizing machine:
1. Coustic Zone
2. Stabilizings Zone
3. Washing Zone
4. Drying Zone
Figure: Mercerising machine
Figure: benniger mercer
Washing Machine
Washing: Washing is the process to remove the impurities from the cloth. Water and soap are used as washing substance and also pH control.
Main chamber of machine:
1. Cold wash chamber
2. Hot wash chamber
Figure: Open-width washing machine
Cold wash chamber
Cold wash chamber: In this chamber the cloth is washed by cold water. It is placed on the two ends of the machine.
Figure: washing machine
Pad steam machine
Pad steam machine: Pad steam machine is one kind of washing machine. The basic difference from washing machine that pad steam machine contains a steamer. In pad steam the cloth pass through the steamer where the cloth is washed by steam at temperature 95-98°C and color fixation these zone. There are 20 rollers which are called dryer. The dryers are rotate by supplying power from motor by chain, gear and belt. The dryers dry the cloth by supplying steam from steam boiler. The clothes are collected by the quick return mechanism.
Figure: Pad steam machine
Application:
1. To mix the color fixation of the cloth
2. To wash the cloth
3. pH control
Cold Pad Batch (C.P.B)
C.P.B: C.P.B or Cold Pad Batch machine is one kind of one color dyeing machine. In C.P.B machine there are spinner roller, steel roller and rubber roller. The spinner roller reduces the folding of cloth and the friction of rubber roller to help the cloth to spin the roller. In C.P.B machine the cloth pass through the roller and below the roller there is a container. The mixture of deices and chemical (NaOH/Urea) by the ratio of 4:1 used to dyeing the cloth. The chemical and deices kept in separated tank and by the help of dozzins pump chemical and deices mixed I 4:1 in a container. From this container using dozzins pump the mixture sprayed on the cloth. By the help of rubber roller the mixture of chemical and deices mixed uniformly on cloth. Finally the cloth is dried by the roller dryer.
Figure: Cold Pad Batch Dyeing Machine
Figure: Cold Pad Batch Machine
Application:
It is used for dyeing (one color) cloth
.
Jigger Machine
Jigger machine: Jigger is a multipurpose machine used for dyeing, scouring, bleaching etc. This machine is used for small purpose generally used for processing sample/short quality dyeing.
Figure: Jigger Machine
Main parts of machine:
1. Hydraulic motor
2. Heat exchanger
3. Coil
4. Electric motor / Pump
Comments
Post a Comment